Healthy vision

Vision disorders

Vitreous opacities
Vitreous opacities are caused by small irregular bodies which float in the vitreous body of the eye. They are called floaters.
What’s the problem?
VITREOUS BODY
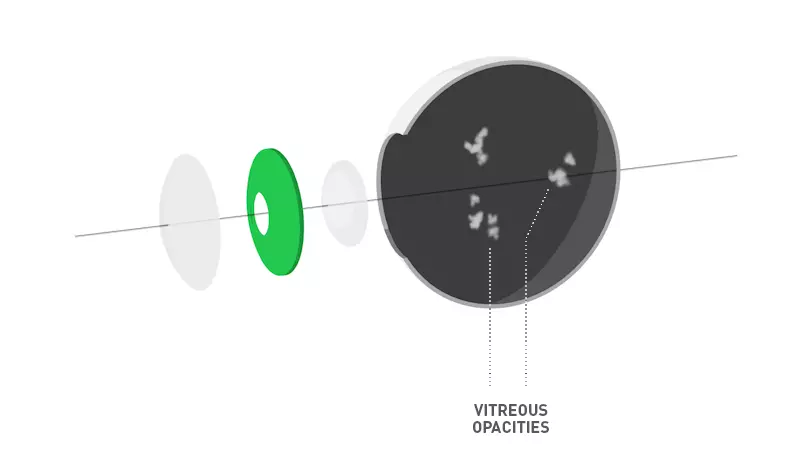
The vitreous body is a jelly-like filling of the eyeball, reminiscent of a raw egg white, which helps it keep its shape. Vitreous opacities most frequently occur when looking at a white surface or at the light. When the vitreous opacities move, they appear in the field of vision.
They can have the shape of specks, stains, threads or cobwebs.
They increase mainly with age, but we can also encounter them in younger patients also after accidents or in the case of short-sightedness. In most cases they are harmless, but they can have a very unpleasant impact on the patient’s life.

What happens during surgery?
LASER VITREOLYSIS
Laser vitreolysis is a non-invasive, painless procedure which is carried out using a special YAG laser and helps remove smaller, localised vitreous opacities.
The eye is first desensitised using drops, then a stabilising contact lens is applied. This keeps the eye open and reduces the speed of its movements. The patient follows the doctor’s instructions and looks at various points in order to remove all localised opacities.
During the procedure, opacities are surveyed using a focusing ray and subsequently removed.
Once the laser ray has been aimed, a micro-explosion of plasma is caused in the vitreous body, which transforms everything nearby into gas. The obstructing shapes disappear or are broken up into smaller pieces and moved to the edge of the field of vision where they cannot be seen.
The procedure takes 15 to 60 minutes and can be performed on both eyes within one day.
The laser treatment usually needs to be repeated on the eye several times, and thus the treatment may include several sessions.
- Laser vitreolysis is not suitable for patients with very dense and large vitreous opacities, infection-related vitreous opacities and opacities located in unsuitable positions (very close to the retina or lens)
- The procedure is usually performed in the central sections of the vitreous body.
- The procedure is performed using a local anaesthetic and is painless.

What can I expect after the procedure
and what post-surgery care is required?
Immediately following the procedure, blurred vision can occur for 3 to 4 hours due to the widening of the pupil and the use of the contact lens
In rare cases, the patient may have the feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the eye, and the eye may run. This feeling results from the slight irritation to the eye caused by the contact lens used during the procedure. These problems usually last only a few hours.
During the post-surgery period, treatment with drops is not usually needed, and no restrictions are required.
Equipment and instruments
Is surgery right for you?
To help you find your way around, we have prepared a brief overview of surgeries available for different types of refractory disorders or diseases. Find out which type of surgery is best for you.
Price list
| VŠZP | DÔVERA | UNION | |
|---|---|---|---|
LASER VITREOLYSIS | 665 € | 665 € | 665 € |
 The price includes 5 sessions
The price includes 5 sessionsTo help you find your way around, we have prepared a brief overview of surgeries available for different types of refractory disorders or diseases. Find out which type of surgery is best for you.